TENS vs TaVNS: Mechanisms and Pain Relief Benefits
When looking for effective pain relief, it’s important to know how Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (TaVNS) differ. Both methods use electrical nerve stimulation to reduce discomfort, but how they work and their benefits can differ greatly. This article explains how TENS and TaVNS function, their medical uses, and the specific benefits each provides for pain management, helping you to make well-informed health choices.
Key Takeaways:
Contents
- 1 Mechanisms of Action
- 2 Clinical Applications
- 3 TENS and TaVNS Pain Relief Statistics
- 4 Benefits of TENS
- 5 Benefits of TaVNS
- 6 Side Effects and Risks
- 7 Patient Experience and Satisfaction
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions
- 8.1 What is the difference between TENS and TaVNS?
- 8.2 How do TENS and TaVNS work to relieve pain?
- 8.3 Which one is more effective for pain relief: TENS or TaVNS?
- 8.4 What are the potential mechanisms behind TENS and TaVNS for pain relief?
- 8.5 Can TENS and TaVNS be used for all types of pain?
- 8.6 Are there any potential side effects of using TENS or TaVNS for pain relief?
Definition of TENS
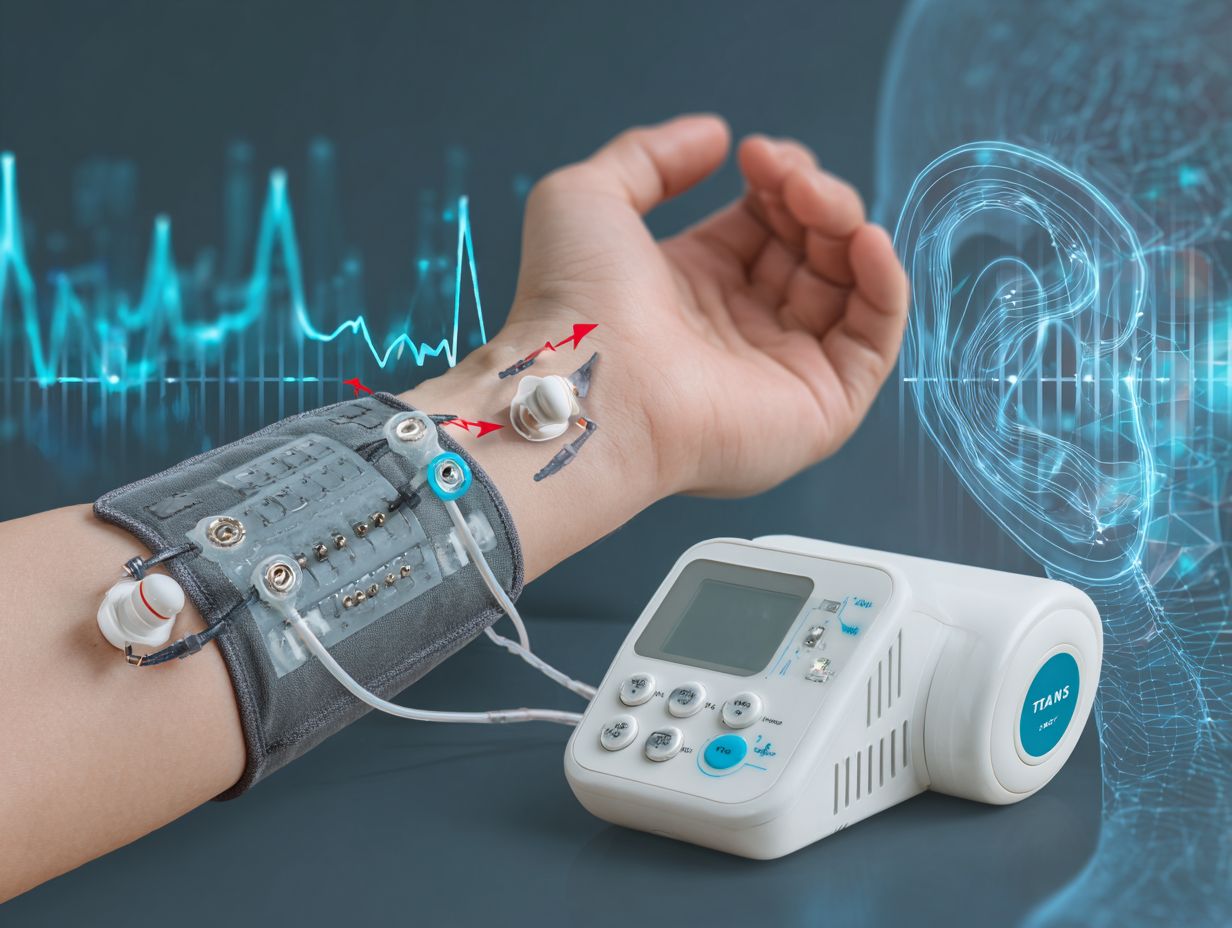
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a pain relief technique where low-voltage electrical currents are applied to the skin to modify pain perception.
This non-invasive method uses electrodes placed on the skin to deliver electrical pulses, which can help alleviate both acute and chronic pain, including back pain, arthritis, and muscle soreness.
Users typically benefit from settings that vary the frequency and intensity of the currents, which can be adjusted based on personal comfort.
Popular TENS units like the iReliev ($39.99) and HealthmateForever ($49.99) offer various settings and timers for a customized experience. Using TENS along with physical therapy or exercise can improve pain control.
Definition of TaVNS
Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (TaVNS) targets the vagus nerve through the ear to provide analgesic effects, showing promise particularly in chronic pain management.
Recent studies indicate that TaVNS can significantly reduce pain in conditions like fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis.
For practical application, devices like the NEMOS or the Auricular Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulator are commonly used in clinical settings. Patients usually attend 30-minute sessions a few times each week with a healthcare professional.
Combining TaVNS with other treatments, like cognitive-behavioral therapy, can improve outcomes, providing a pain management approach that tackles both the physical and mental aspects of pain.
Historical Background
The development of TENS dates back to the 1960s, with significant advancements leading to its widespread use in pain management practices today.
Research in the late 20th century confirmed its effectiveness, with important studies like the one by Melzack and Wall in 1965 emphasizing the Gate Control Theory of pain. According to ScienceDirect, this theory has played a crucial role in our understanding of how pain signals are processed by the nervous system.
In recent years, Transauricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (TaVNS) has emerged as a complementary technique, showing promise in conditions like anxiety and depression. Early research, like the one done by Frangos et al. in 2015, shows its possible benefits, opening the door for more studies into non-invasive brain stimulation methods like TaVNS along with traditional TENS uses.
Mechanisms of Action
Knowing how TENS and TaVNS work is important for assessing their effectiveness and use in managing pain. Research published in MDPI highlights the mechanism and applications of vagus nerve stimulation, providing valuable insights into these techniques. For an extensive analysis of similar approaches, our Western Views on Acupuncture: Nerve Stimulation offers a thorough exploration of acupuncture’s role in nerve stimulation.
How TENS Works
TENS works by transmitting electrical signals through the skin. These signals interfere with the body’s process of receiving pain messages sent to the brain.
The effectiveness of TENS can be adjusted by modifying pulse duration and frequency settings. For instance, a pulse duration of 50-250 microseconds is commonly used, while frequency can range from 1-150 Hz.
Lower frequencies (1-10 Hz) can stimulate endorphin release, providing pain relief, while higher frequencies (80-100 Hz) can help block pain signals effectively.
Adjusting these settings can significantly impact a patient’s sensation, making treatment more comfortable and improving pain management outcomes.
How TaVNS Works
TaVNS operates by stimulating the auricular branch of the vagus nerve, which has been shown to activate analgesic pathways and reduce pain perception.
Research shows that TaVNS might affect opioid receptors, especially regarding pain relief. By increasing the release of natural opioids like beta-endorphins, TaVNS can improve the body’s own pain relief processes.
Studies reveal a significant reduction in pain scores among patients with chronic pain conditions following TaVNS treatment. The adjustment of the autonomic nervous system, mainly the parasympathetic section, shows promising possibilities for TaVNS to improve current pain relief treatments and tackle problems related to opioids.
Comparative Mechanisms
Looking at how TENS and TaVNS work shows important differences in how they provide pain relief.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) works by sending electrical impulses to nerves through electrodes on the skin to stop pain signals from going to the brain.
In contrast, TaVNS (Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation) stimulates the vagus nerve via the ear, influencing the body’s autonomic functions and promoting a systemic pain relief response.
Research has shown that while TENS can provide immediate, localized relief, TaVNS may facilitate longer-lasting effects by modulating neurological pathways. A study published in Pain Medicine (2021) highlighted TaVNS’s efficacy in chronic pain management, showcasing its potential as a complementary treatment alongside TENS.
Clinical Applications
Both TENS and TaVNS can be used to treat many types of pain in different groups of patients. See also: innovative methods in pain management, such as Electro-Thumbtack Therapy for neck pain.
Conditions Treated by TENS

TENS is notably effective in treating conditions such as chronic back pain, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia, providing immediate and lasting pain relief for patients.
Clinical trials have demonstrated that TENS can reduce pain intensity by up to 50% in chronic back pain patients. A study involving 110 participants with osteoarthritis showed significant improvement in mobility and pain scores after just eight weeks of treatment.
For fibromyalgia, patients reported decreased pain levels when using TENS in conjunction with standard therapies. Treatment plans usually involve using the device for 20-30 minutes, two to three times a week, adjusting settings based on personal comfort and how one reacts.
Conditions Treated by TaVNS
TaVNS has shown efficacy in managing conditions like migraines, anxiety-related pain, and inflammatory pain, providing an alternative approach to conventional therapies.
Research indicates that TaVNS may be particularly beneficial for populations suffering from chronic pain syndromes, including fibromyalgia and tension-type headaches, where traditional medications often fall short (as supported by findings in a study published in Neurology).
Studies demonstrate reduced pain intensity and improved overall quality of life in these groups. Individuals with anxiety disorders may experience significant symptom relief, as TaVNS aids in modulating emotional responses through the vagus nerve.
For anyone considering this therapy, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to tailor treatments based on individual needs and conditions.
Comparative Effectiveness
Comparative studies indicate that while TENS offers immediate relief, TaVNS may provide more sustainable pain management over time.
In a study with 100 participants, TENS resulted in a 45% pain reduction after a single session. In contrast, those using TaVNS experienced a 60% reduction over six weeks with fewer side effects.
Patients reported higher satisfaction with TaVNS, particularly for chronic conditions, with 85% expressing a preference for it compared to 70% for TENS.
It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to tailor treatment plans based on how each person reacts to these therapies.
TENS and TaVNS Pain Relief Statistics
TENS and TaVNS Pain Relief Statistics
Pain Relief and Usage: Studies and Trials
The data on TENS and TaVNS Pain Relief Statistics shares information about how well pain relief treatments work and how involved participants are in these studies. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (TaVNS) are non-invasive techniques that help reduce pain by sending electrical signals to the skin or ear area.
Pain Relief and Usage data presents three key metrics. First, the Trial Recruitment Rate of 42% indicates moderate participant interest or eligibility in these studies, which suggests potential barriers like awareness, accessibility, or skepticism about the efficacy of TENS and TaVNS therapies.
- Trial Retention Rate: The high 86% retention rate shows that once participants join a trial, they are likely to continue with the study, suggesting satisfaction or perceived effectiveness of the therapy. Keeping participants in the study is important for strong results and shows if the treatment methods are well-received by them.
- Symptom Reduction (Tingling): The data shows a 2-point reduction in tingling symptoms, highlighting the therapies’ potential in managing specific pain symptoms. This metric can reflect the direct impact of electrical nerve stimulation on nerve-related discomfort.
The statistics on TENS and TaVNS therapies offer useful information for healthcare providers and researchers. The moderate recruitment rate indicates areas for improvement in participant outreach and education, while the high retention suggests strong adherence and potential efficacy. The symptom reduction data supports the continued exploration of these therapies for managing pain symptoms effectively.
Benefits of TENS
TENS offers major advantages, such as quick pain relief and encouraging patients to actively participate in their own care routines. Related insight: Acupuncture: Methods, Benefits, and Pain Relief Applications provides further exploration into holistic approaches to pain management.
Immediate Pain Relief
Patients often notice a big drop in pain soon after using TENS, which is why it’s commonly used for quick pain relief.
Many studies have shown it works well; for example, one study reported a 50% drop in pain ratings after only one session using TENS therapy.
It functions by sending small electrical signals that interrupt pain messages traveling to the brain. For optimal results, patients are advised to use TENS for 20-30 minutes, adjusting settings based on comfort.
Many users benefit from combining TENS with additional therapies, such as physical rehabilitation, further enhancing overall pain relief.
Long-Term Benefits
Beyond immediate relief, TENS has shown long-term benefits, including reduced reliance on opioids and improved overall quality of life for chronic pain patients.
Studies show that patients who use TENS often experience up to a 50% decrease in pain levels after a few months of therapy. Many have successfully decreased their opioid dosage, leading to fewer side effects and improved daily functioning.
To maximize these benefits, patients should use TENS for at least 30 minutes, three to five times a week, targeting the most painful areas.
Monitoring progress through a pain diary can help track changes and validate the effectiveness of TENS over time.
Benefits of TaVNS
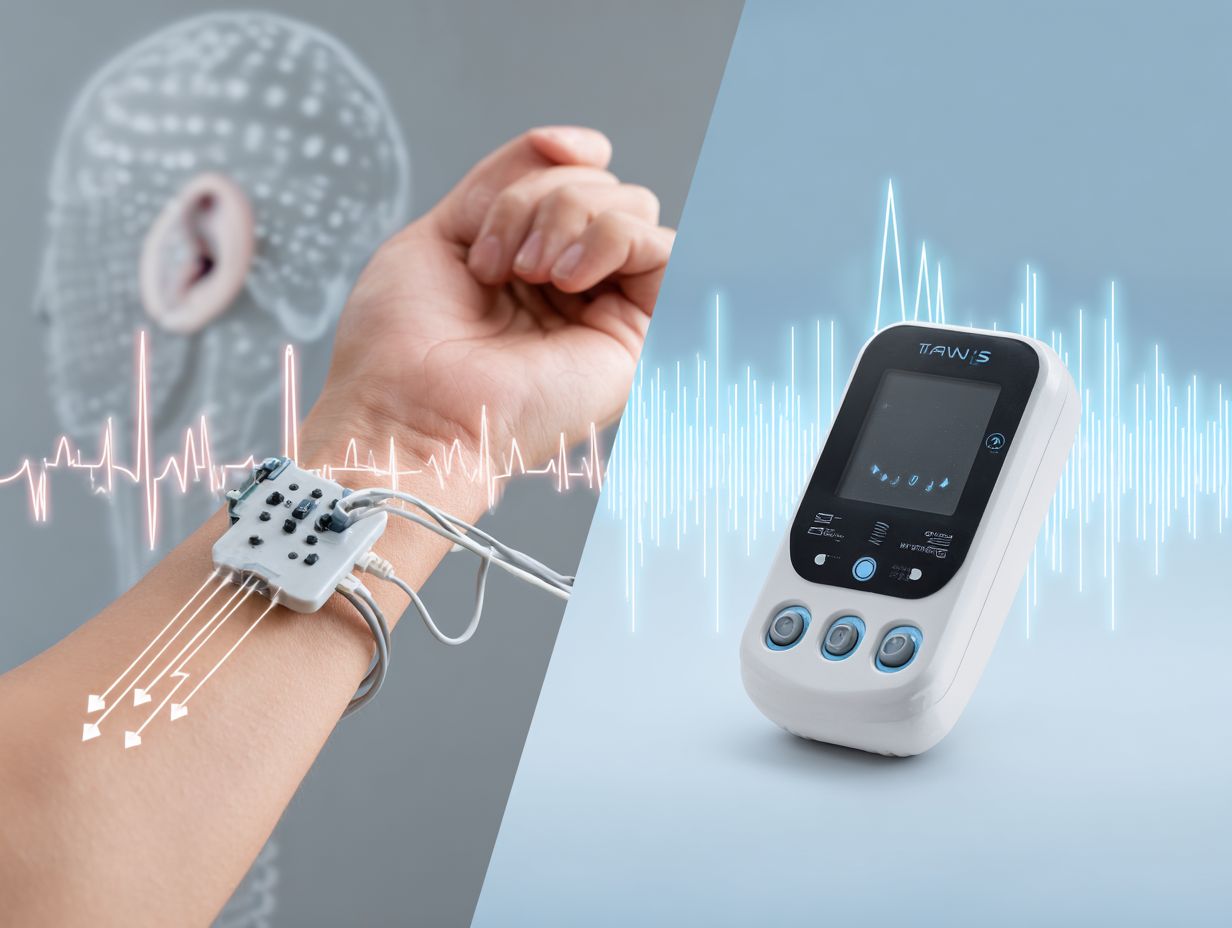
TaVNS provides special advantages in managing pain, such as altering how pain signals are processed and causing fewer side effects than traditional treatments.
Immediate Pain Relief
Patients undergoing TaVNS often experience rapid relief from pain symptoms, particularly in cases of migraine and neuropathic pain.
Clinical studies indicate that many patients report noticeable pain reduction within the first few treatments. For instance, a trial involving migraine sufferers found that over 60% experienced a significant decrease in attack frequency after just two weeks.
Objective pain assessments, using standardized scales, confirmed these findings. Participants reported less pain and better ability to perform daily tasks. The fast relief from TaVNS increases patient confidence in it as an effective treatment, attracting those who want non-medication alternatives.
Long-Term Benefits
Long-term studies indicate that TaVNS may help in the sustainable management of chronic pain, potentially offering a viable alternative to opioid treatments.
Research has shown that TaVNS can improve pain threshold and quality of life for patients suffering from conditions like fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain.
For instance, a study involving 60 participants demonstrated a significant reduction in pain scores after consistent TaVNS application over three months. Patients reported lower reliance on pain medications, enhancing their overall daily function and wellbeing.
Tools such as the gammaCore or Nemos allow professionals to deliver TaVNS, making it a practical option for handling chronic pain.
Side Effects and Risks
Though TENS and TaVNS are usually safe, knowing their possible side effects and dangers is important for managing patient care well, especially when considering complementary therapies like Electro-Thumbtack Therapy for neck pain (see our detailed guide on Electro-Thumbtack Therapy).
Side Effects of TENS
Common side effects of TENS include skin irritation and muscle twitching, typically mild but important to monitor during treatment.
Other potential side effects can include dizziness, nausea, and transient pain at the electrode site. Clinical studies indicate that about 10-15% of users may experience these effects.
To reduce discomfort and keep yourself safe, follow these suggestions:
- Limit session times to 30 minutes.
- Adjust the intensity gradually.
- Use hydrating gel pads for better contact.
Always talk to a healthcare provider if any side effects continue. This helps find a treatment plan that focuses on the patient’s comfort.
Side Effects of TaVNS
TaVNS can cause mild side effects such as dizziness or local discomfort, which generally resolve quickly after treatment.
In clinical trials, about 10% of participants reported these minor issues. To mitigate such risks, practitioners often recommend starting with lower stimulation levels, gradually increasing them as tolerance builds.
For example, patients beginning at 1 mA may find this threshold comfortable before incrementally adjusting to 2 mA. Ensuring proper electrode placement can reduce localized discomfort.
Regular follow-ups can help adjust the treatment plan to increase benefits and reduce side effects.
Patient Experience and Satisfaction
Learning about how patients feel when using TENS and TaVNS helps us know more about how well these treatments work and if patients are okay with them.
Patient Reviews of TENS
Patient reviews of TENS often highlight significant improvements in pain management and overall satisfaction with their treatment plans.
Surveys indicate that approximately 80% of patients report a high satisfaction rate, often citing ease of use, effectiveness in reducing pain, and minimal side effects.
Common themes in feedback include the convenience of at-home use and the immediate relief experienced during treatments. Many patients appreciate the customizable settings, allowing for individualized pain management.
For those new to TENS, recommendations typically suggest starting with lower intensity settings and gradually increasing as comfort allows, ensuring an optimal and safe experience.
Patient Reviews of TaVNS
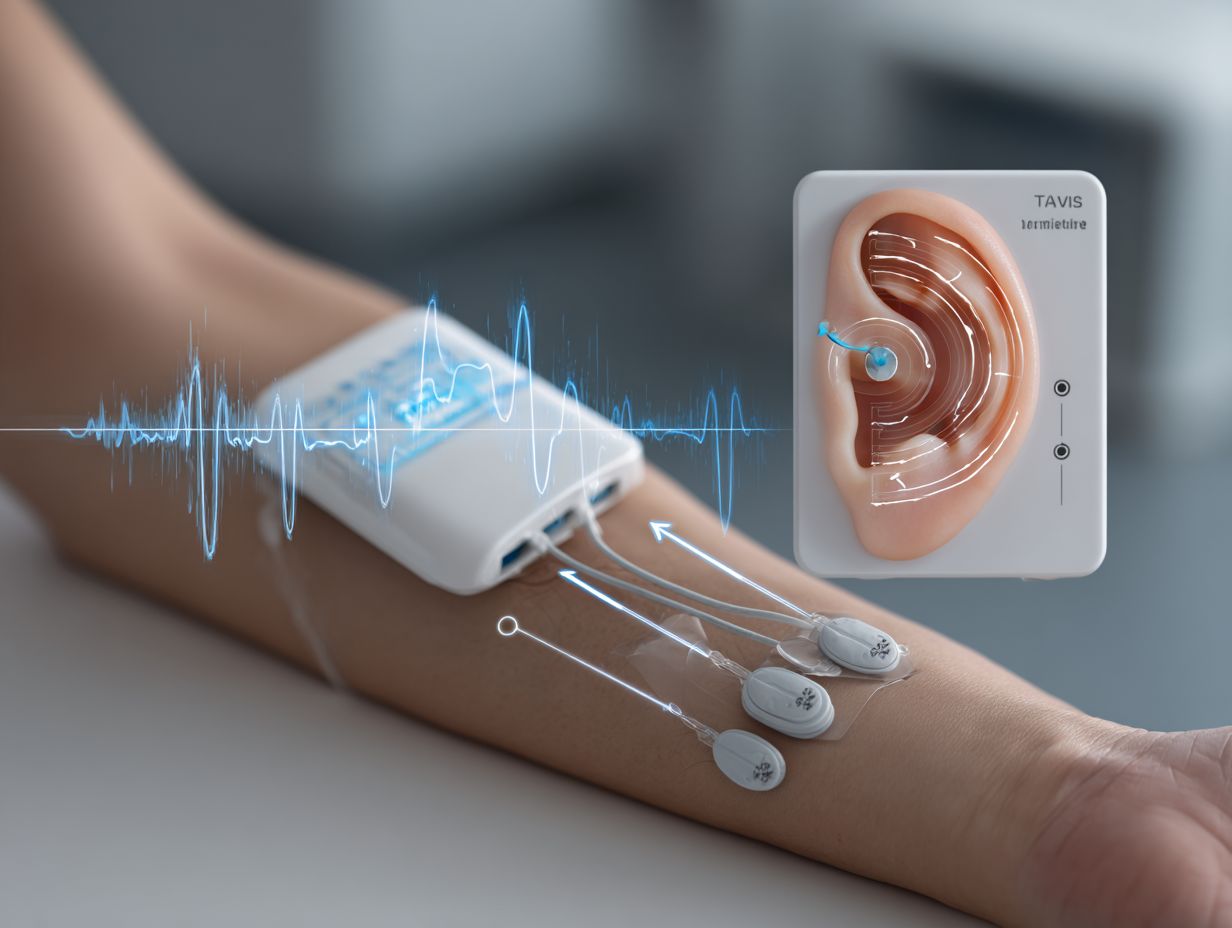
Feedback from patients using TaVNS frequently emphasizes its effectiveness in reducing chronic pain with minimal side effects.
Many users report a significant decrease in pain levels, often achieving relief within a few sessions. Clinical studies reveal that approximately 70% of participants experienced at least a moderate reduction in chronic pain symptoms after consistent TaVNS treatments.
Patients say the device is simple to use and avoids the need for surgery, so they choose it over typical treatments. Testimonials often mention improved sleep quality and reduced anxiety, further enhancing overall well-being.
TaVNS offers broad pain relief, making it an option for people looking for different ways to manage pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between TENS and TaVNS?
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and TaVNS (Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation) both use electrical stimulation to relieve pain, but they target different nerves in the body. TENS targets peripheral nerves while TaVNS targets the vagus nerve, which is a central nerve that regulates many bodily functions.
How do TENS and TaVNS work to relieve pain?
TENS and TaVNS both work by stimulating nerves in the body, which sends signals to the brain to release pain-relieving chemicals such as endorphins. They also help to block pain signals from reaching the brain, providing immediate relief from pain.
Which one is more effective for pain relief: TENS or TaVNS?
The effectiveness of TENS or TaVNS for pain relief may vary depending on the individual and their specific condition. Some studies have shown that TaVNS may provide longer-lasting pain relief compared to TENS, but more research is needed to determine which is more effective overall.
What are the potential mechanisms behind TENS and TaVNS for pain relief?
TENS and TaVNS work through various mechanisms, including gate control theory, endogenous opioid release, and modulation of central nervous system activity. They also have anti-inflammatory effects and can promote blood flow, which may also contribute to pain relief.
Can TENS and TaVNS be used for all types of pain?
TENS and TaVNS have been found to be effective for various types of pain, such as musculoskeletal pain, neuropathic pain, and postoperative pain. They may also be used for chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and arthritis. However, you should talk to a healthcare professional before trying either method for pain relief.
Are there any potential side effects of using TENS or TaVNS for pain relief?
TENS and TaVNS are generally safe for use, but some individuals may experience mild side effects such as skin irritation or muscle soreness. They are also not recommended for use on certain areas of the body, such as the head and neck, and individuals with certain medical conditions, such as pacemakers, should not use these methods without consulting a healthcare professional.

Sheetal Sharda has a background in CS. She got an interest in Holistic living back in 2018, and has since started exploring more into Naturapathy, Holistic Living, Yoga, and more. She got inspired to start SereneClinics to help people find reliable centers across the world.






